Bromine
| Bromine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Info | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic Symbol | Atomic symbol::Br | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic Number | Atomic number::35 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic Weight | Atomic weight::79.904 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical series | halogen | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | Reddish-brown 
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group, Period, Block | 17,4,p | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Ar] 3d10, 4s2, 4p5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2,8,18,7 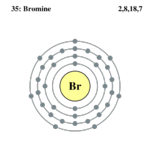
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number | CAS number::7726-95-6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase | Liquid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density | Density::3.119 g/ml | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | Melting point::265.95K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | Boiling point::331.93K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of Bromine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All properties are for STP unless otherwise stated. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Bromine is a chemical element classified as a halogen and known by the chemical symbol Br. It is the only nonmetal element that remains liquid under normal conditions. Bromine is a reddish-brown color with a vapor of similar color and a horrible odor. Bromine is similar to other halogens, but quite unordinary and unique among all the elements.
Though used much more frequently a few decades ago, Bromine is used commercially throughout the world today. In gas and liquid form, Bromine is toxic to human skin, eyes, and throat, but is also useful in many ways that benefits humans. Though useful and used a lot, Bromine does not occur naturally and is hard to find in nature, most often appearing as Bromine salts in crustal rock.[1]
Properties
Bromine appears as a reddish-brown liquid, at proper temperature, with a similarly colored vapor and a horrible odor. It stands as the only nonmetal element that exists as a liquid under ordinary conditions, also evaporating as a red vapor at standard temperature with a strong offensive odor resembling that of Chlorine. Chemically, Bromine appears less appealing than Chlorine and Fluorine, but is far more active than Iodine. Bromine compounds are very similar to the compounds of other halogens. Bromine is also soluble in organic solvents and in water, and will dissolve. Bromine may also react with water, creating hydro bromic acid.[2]
Atomically, each Bromine atom contains 35 protons, corresponding with its number on the periodic table of elements. There are 47 variations of Bromine, also known as bromine isotopes, and 29 of them are radioactive. Each bromine isotope is marked by the number of neutrons in each atom, all of which are different. Along with the 47 bromine isotopes, there are 16 bromine isomers, which differ structurally.[3]
Occurrences
Free elemental Bromine does not occur naturally, but exists exclusively as bromide salts diffused in crustal rock. Bromide salts have accumulated in sea water at over sixty five ppm (parts per million), which is far less than Chloride. It may be recovered from bromide-rich brine wells and from the waters of the Dead Sea. It exists in the Earth's crust at a concentration of about 0.4 ppm, placing it as the 62nd most abundant element. In soil, the bromine concentration normally varies between 5 and 40 ppm, skyrocketing to a concentration of about 500 ppm in volcanic soil. [4]
The concentration of bromine in the atmosphere is terribly low, coming in at only a few ppt (parts per notation). However, many organobromine compounds can be found in small amounts in nature. China, Israel, and the U.S. all possess large bromine reserves; the U.S. laying claim to the largest.[5]
Uses
There are several industrial uses for Bromine; most are produced from Bromine but some are produced from Hydrogen bromide, made by burning Hydrogen in Bromine. The largest commercial use of Bromine is brominated flame retardants. These brominated flame retardants, when burned, produce hydro bromic acid to interfere with the chain reaction of oxidation in the fire. Many gaseous brominated halomethane compounds are non-toxic and make superior fire suppressants by acting directly with radical reactions to terminate the free radical chain reactions of combustion. These are most effectively used in confined spaces like submarines, airplanes, and space crafts; but due to expense and production their use has been greatly decreased. Bromochloromethane, bromochlorodifluoromethane, and bromotrifluoromethane are still used in aerospace and militant fire suppression.
The second most important use of bromine is water purification, as an alternative to chlorine. Brominated compounds are used in swimming pools and hot tubs for water treatment and to control algae and bacterial growth in industrial processes.[6] Ethylene bromide was a popular gasoline additive in the 1970s, but its use has greatly decreased due to environmental control. Deadly methyl bromide was a widely used pesticide, to fumigate soil and housing by tenting, but due to the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone they have not been used since 2005. In the 19th and 20th centuries, bromide compounds were often used as sedatives. In 1975, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration removed bromide from over-the-counter sedatives. Today, simple salt bromides are used as anticonvulsants in veterinary and human medicine throughout the world.[7]
Bromine in Ozone Depletion
Since the 1970s, the ozone layer has decreased about four percent in volume every decade. Bromine is one of the many contributors to this major decline. Bromine and Chlorine are two of the most commonly known factors of this major decline. Though Chlorine concentrations in the stratosphere are much larger than Bromine concentrations, about 150 times larger, Bromine is 97 times as damaging to the ozone layer as Chlorine is. The reason for this is that, even though there is not really a stable reserve for Bromine in the stratosphere, Hydrogen Bromide and Bromine Nitrate are easily photolyzed so that Bromine is almost always in a form that can react with the ozone layer. So, because of this, even though Bromine concentration levels are much lower that that of Chlorine and often considered less important, Bromine is still a major contributor to ozone depletion and should always be taken into account. However, one of the main processes in which Bromine damages the ozone layer involves Chlorine. So if the stratospheric Chlorine concentration levels were to decrease, in turn, the Bromine pathways to damaging the ozone layer would be slowed down.[8] Though truly, it is not the process that causes the most damage, but the atom itself. One Bromine atom can destroy about 300,000 ozone atoms before being removed from the stratosphere. This negative effect on the ozone layer is one of the major reasons for the decrease in Bromine usage since the 1960s.[9]
Video
The Discovery of Bromine
References
- ↑ Bromine- Br LENNTECH. Web. 10 August 2014 Date of Access. Unknown Author.
- ↑ Unknown Author. Bromine- Br LENNTECH. Web. 10 August 2014 Date of Access.
- ↑ Orwell, Mark. Properties & Uses of Bromine eHow.com. Web. 10 August 2014 Date of Access.
- ↑ Unknown Author. Bromine-Discovery, Occurrence and Applications of Bromine AZoM.com. Web. 7 August 2006 Date of publication.
- ↑ Unknown Author. Bromine Wikipedia. Web. 6 July 2014 Date of Access.
- ↑ Unknown Author. Bromine-Discovery, Occurrence and Applications of Bromine AZoM.com. Web. 7 August 2006 Date of publication.
- ↑ Unknown Author. Bromine Wikipedia. Web. 6 July 2014 Date of access.
- ↑ Parson, Robert. How Does Bromine Affect Ozone? StasoSphere.com. Web. 8 July 2014 Date of Access.
- ↑ Unknown Author. The Process of Ozone Depletion U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Web. 19 August 2010 Date of Publication.
| ||||||||||||||
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn | ||||||||||
| Fr | Ra | Ac | Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Uut | Fl | Uup | Lv | Uus | Uuo | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


