Relatividade especial
A teoria da relatividade especial foi publicada por Albert Einstein em 1905. A teoria trata de um caso especial em que os efeitos da gravidade podem ser ignorados, portanto, é chamada "especial." Einstein incorporou mais tarde a gravitação na teoria da relatividade geral.
Postulados
A Relatividade Especial tem dois postulados a partir do qual se desenvolve.
- As observações dos fenômenos físicos são as mesmas para todos os observadores inerciais
- A velocidade da luz no vácuo (c) é a mesma para todos os observadores inerciais. É a mesma em todas as direcções, independentemente da velocidade da fonte ou o observador.
Diagrama Espaço Tempo
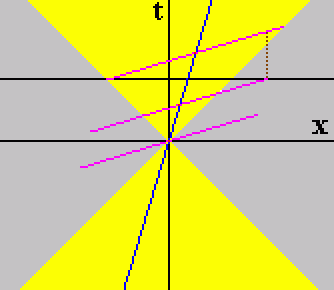
Este é um diagrama de espaço de tempo; também chamado de diagrama Minkowski ele mostra a relação entre os referenciais inerciais. De tal modo que se o observador S' está movendo com uma velocidade v em relação a S. A superposição resultante tem os eixos de S' inclinada de tal modo que a inclinação do eixo do tempo é v / c e a inclinação do eixo espacial é c / v.
Contração do comprimento
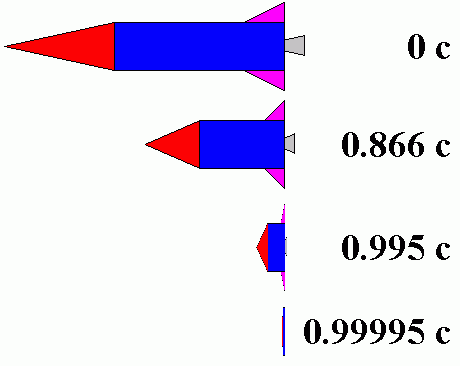
A contração do comprimento relativista é um encurtamento do comprimento de um objeto na direção do movimento relativo, como ilustrado acima.
- Fórmula para a contração do comprimento relativista.
- v é a velocidade relativa.
- c é a velocidade da luz.
- L é o comprimento de repouso.
- L' é o comprimento a uma velocidade v.
- Diagrama de espaço-tempo mostrando contração do comprimento relativista.
Um exame de um diagrama de espaço-tempo mostra que esse efeito é causado por uma relação de inclinação entre dois referenciais no espaço-tempo. A área amarela é um cone de luz. A linha preta são os eixos de espaço (x) e tempo (t). A linha azul é o eixo de tempo do quadro S'. A linha roxa é o eixo espacial de um navio no quadro S'. Observe que no quadro S' o cone de luz atinge ambas as extremidades do navio no momento, enquanto, eles não estão no quadro S. Isso porque quando o observador S está olhando para as duas extremidades do navio está olhando para pontos diferentes no quadro S' na linha do tempo. Portanto, a extremidade dianteira do navio S' como visto pelo observador S não se moveu até a extremidade da popa, o que resulta no navio S' sendo reduzido ao observador S.
É preciso notar que um observador no quadro S' verá objetos no quadro S com a mesma contração de comprimento.
Dilatação do tempo
- Relógio de luz em repouso.
O conceito de dilatação do tempo é amplamente baseado em um relógio com um pulso de luz indo de um emissor (vermelho) para um receptor. (azul) o tempo de viagem é uma unidade de tempo.
- Relógio de luz em movimento.
Quando o relógio está em movimento, o pulso de luz tem que viajar mais para chegar ao detector e, como a velocidade da luz é constante, leva mais tempo para que o pulso de luz chegue ao detector. Isso se traduz na fórmula da dilatação do tempo para o movimento relativo.
- v é a velocidade relativa.
- c é a velocidade da luz.
- t é o comprimento restante.
- t' é o comprimento na velocidade v.
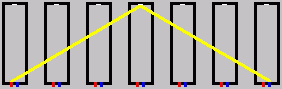
Agora, este novamente funciona nos dois sentidos, os resultados no que é chamado de paradoxo dos gêmeos. No entanto, é simples ilustrar por que o gêmeo fazendo a viagem demoraria menos.
Consider a space ship going from Earth to the nearest star system; 4.45 light years away; at 0.866 c. The above image shows the the ship with its 0.5 length contraction. To an observer on Earth the trip will take 5.14 years, producing a round trip time of 10.28 years.
However to the ship's crew the stars and the distance between them will be shortened in the direction of motion to 0.5 of what is observed on Earth, resulting in a travel distance of only 2.23 light years and a corresponding 2.57 year travel time. This produces a round trip time of only 5.14 years. Thus the ship's crew would experience less time than those on Earth.
If one of the astronauts on the ship had a twin that stayed on Earth. he would return home to find his brother about 5 years older than himself.
Now this takes care of the physical affect of time dilation but it does not reconcile how each twin would observe the other during the trip. The solution to this observational problem can be found in the relativistic Doppler effect. It includes the affects of both time dilation and distance, hence we can calculate just how fast each twin will observe time to flow in the other's reference frame.
- The back line is Earth's path through space time.
- The dark blue line is ship's path outward path through space time.
- Purple line is its path return path through space time.
- The green dots are equally spaced points in time within their respective frame of reference.
- The red lines are the path of light between Earth and the ship during the outward trip.
- Light blue dots arrival point of light.
On the outward trip the relativistic Doppler effect shows each twin would see 1 second pass for the other twin for every 3.7 seconds of his own time. The twin on the ship would see this effect for 2.57 years, as such he would see his twin age 0.69 years. However since the light showing the ships arrival would not arrive at Earth for 4.45 years, the twin on Earth would see this effect for 9.59 years, as such he would see his twin age 2.57 years.
- Blue lines are the path of light between Earth and the ship during the return trip.
- Light blue dots arrival point of light.
- Left image shows Earth to ship.
- Right image shows ship to Earth.
On the inward trip the relativistic Doppler effect shows each twin would see 3.7 seconds pass for the other twin for every second of his own time. The twin on the ship would see this effect for 2.57 years, as such he would see his twin age 9.59 years, for a total of 10.28 years. However since the light showing the ships departure would not arrive at Earth for 4.45 years, the twin on Earth would see this effect for only 0.69 years since ship returns after 10.28 years, as such he would see his twin age 2.57 years, for a total of 5.14 years.
- This diagram shows the light path's for both legs of the flight.
- Left image shows Earth to ship.
- Right image shows ship to Earth.
- Note that there is more blue on the left and more red on the right. That is why the ships crew sees the Earth age more than they do.
Thus the twin paradox is resolved both in terms of the physical affect of time dilation and the observation of both twins, since both the physical affect and observation agree on how much each twin would age.
Relativistic Mass
- Formula for relativistic mass.
- Formula 1
It from this that we get Einstein famous equation for the equivalence of mass and energy. E = mc2
- Formula for relativistic kinetic energy.
- Formula 2
It turns out that when v << c that the classical formula Ficheiro:Kec.png is a good approximation of relativistic kinetic energy. So the relativistic increase in mass with velocity is a result of the object's kinetic energy.
Biblical Significance
Special Relativity has been criticized by some Christians. It is claimed that by removing absolute space and time, it is there by implying no moral absolutes. First of all this is illogical since there is no real connection between the two. Furthermore Special Relativity does have an absolute, the speed of light.
1 John 1:5 compares God to light, and according to Special Relativity no matter how fast you accelerate you will always fall equally short of the speed of light. Similarly, no matter how hard you work you will always fall equally short of the glory of God.
Special Relativity shows that time is an integral part of the structure of the universe, and not just the perceptions of a sequence of events. The result is that anything outside the universe would be timeless (or have its own time). God, as the creator of the universe, must exist outside His creation, and therefore by definition must be eternal and transcendant.
References
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||