Silver bromide
| Silver bromide | |
|---|---|
 | |
| General | |
| Systematic name | Silver(I)Bromide |
| Molecular formula | AgBr |
| SMILES | [Ag]Br |
| Molar mass | Molar mass::187.78 g/mol |
| Appearance | =Light Yellow Powder |
| CAS number | CAS number::7785-23-1 |
| Properties | |
| Density and phase | Density::6.473 g/ml |
| Solubility in water | 12 X 10-6 g/100 ml |
| Melting point | Melting point::432°C |
| Boiling point | Boiling point::700°C |
| Structure | |
| Molecular shape | Linear |
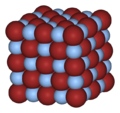
| Crystal structure | cubic |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | Material safety data sheet |
| Main hazards |
Harmful by ingestion, inhalation, |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | Not apllicable |
| R/S statement | R: R22 S: S24, S25 |
| RTECS number | NO data |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Silver(I) fluoride Silver chloride Silver iodide |
| Other cations | Copper(I) bromide Mercury(I) bromide |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Disclaimer and references | |
Silver Bromide (AgBr) is an inorganic compound that commonly exists as a light yellow powder. It has a linear structure and a cubic structure that needs larger amount of bromine to make a cube. Silver has to fill in the rest. It does not get harm to our body. This compound use of photographic emulsion and use of application of lenses and windows that makes light. [1]
Properties
Crystal Structure Silver Bromide has the same structure as Sodium Chloride which is a linear structure and has faced centered cubic structure. These large ions which is Bromide are arranged in a cubic structure, while the smaller silver ions fill in the cubic.[1]
Solubility Silver Bromide has a large range of solubility, which is about 6x107times greater than that of AgI. This may give us ideas which has more solubility in their compounds.[1]
Semiconductor Properties Silver Bromide can be heated within 100 degrees which is in melt point. By this all the conductivity and electronic energy gap increased. It means crystal is instability. This behavior semi-conductor is distributed to a temperature.[1]
Perparation and Reaction
Most of the compounds can be found in mineral form, Silver Bromide is typically reacts with alkali bromide, potassium bromide and silver nitrate. These form AgNO3 (AQ) + KBr (AQ) → AgBr (S) + KNO3 (AQ). This can be prepared as elements. However, it is less convenient.[1]
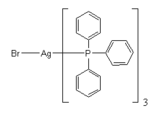
Silver bromide reacts with ammonia to generate a variety of many complexes and also reacts with triphenylphosphine, which is shown as an example here:
AgBr + nNH3 → Ag(NH3)21+{AgBr(NH3)2}{AgBr2(NH3)2}1-{AgBr(NH3)}{AgBr2(NH3)}1- [1]
Uses
Photography Photographic process have been developed in the Mid 1800's. Which silver bromide compound revealed the photographic mechanism. Silver bromide was result of deviation from an ideal crystal structure.[1] Photographic is made of silver bromide that suspends into a thin layer of gelatin which is called photographic emulsions. Sometimes, when negative film is processed, they convert the emulsion layer into metallic silver.[2]
Hazard Identification
Irritation to eyes, skin, and upon ingestion and inhalation have been recorded. When we get that into our bodies, firstly, we need to flush water for 15 minutes to clean eyes or skin directly. We need fresh air and to drink a lot of water. [3]
Media
References
| ||||||||||||||