Paraffin
| Paraffin | |
|---|---|
| |
| General | |
| Other names | Paraffin wax, Petroleum wax [1] |
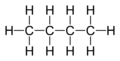
| Molecular formula | CnH2n+2 |
| Appearance |
White translucent tasteless |
| CAS number | CAS number::8002-74-2[1] |
| Properties | |
| Density and phase | 0.88 - 0.92 g/ml, solid[1] |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble[1] |
| Melting point | 47 - 65°C [1] |
| Boiling point | 370°C [1] |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | Material safety data sheet |
| Main hazards |
Digestion and inhalation |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 199°C [1] |
| R/S statement | S: 24/25[1] |
| RTECS number | RV0350000 [1] |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Disclaimer and references | |
Paraffin wax, also known as petroleum wax, is a white, translucent, tasteless, and odorless solid material that has various uses such as in manufacturing of candles and medical uses.It does not have a definite composition, but is a linked chain of hydrocarbons. The molecular formula is CnH2n+2.
Properties
Paraffin wax is a complex combination of solid straight-chain hydrocarbons. It is colorless or white, and somewhat translucent. It is also odorless and tasteless. [1] It is distinguished from the microcrystalline wax which is also derived from petroleum by its large, well formed crystals [5]
The physical state of paraffin wax is highly dependent upon factors like temperature and pressure. The length of the longest, uninterrupted linear alkane constituent also determines the physical properties. Paraffin waxes with high molecular weight can be hard and brittle, whereas paraffin waxes with lower molecular weight are generally malleable. The melting point depends on how well the molecules fit into a crystal lattice; increased content of longer, heavier alkanes increase the melting point, whereas increased branched alkane content decreases the melting point. [6]
Synthesis
Paraffin wax is derived from petroleum hence its other name, petroleum wax. [5] Paraffin wax precipitates readily from petroleum on chilling. Technical progress has served only to make the separations and filtration more efficient and economical. [7]
Slack wax, a mixture of oil and wax, is refined from lubricating oil. It is refined further to obtain petroleum wax. The first step of the refinery operation is crystallization in which the slack wax is heated, mixed with solvent and then cooled. Through this process, wax is crystallized and oil is left out in solution. To separate the wax, the solution is filtered by rotary drum filters through two or three stages. The solvent-free wax is decolored and deodorized by a vacuum stripping tower. Fully refined paraffin waxes are blended together to give certain desired properties. [8]
Uses
Paraffin waxes have a tendency to be brittle and therefore are not very useful for industrial purposes. [9] One of the oldest uses of paraffin wax is candles.[10] Paraffin candles are the most common type of candles, having most fragrances and dyes formulated for them. [11] Another common use of paraffin wax is the manufacturing of crayons. Liquid paraffin and ground pigment are mixed together to create colored crayons. [12] Chewing gum also has a base of paraffin wax. After spruce gum of American Indians were sold commercially, they were gradually replaced by paraffin wax gum. Nowdays, sweetened and flavored paraffin wax is used in the production of chewing products. [13]
Paraffin wax can be used as a treatment for arthritis by providing moist heat to hands or feet easing the pain and stiffness. [10] Petroleum jelly, the main ingredient in vaseline, is made out of paraffin wax and is commonly used to cure dehydrated, flaky skin, rashes, etc. [14] They are also used in spa treatments called paraffin pedicures in which paraffin wax is applied to the feet in order to moisturize the skin on the feet. [15] It also serves as a thickener, or an emulsifier in cosmetics. [16]
History
Paraffin wax was used as a medical treatment in the past. Romans were known to melt paraffin wax down and then apply it while still very warm to the body before giving a massage. French doctors used melted paraffin wax to protect wounds to help them heal and avoid infections. In World War I the British used the wax for orthopedic issues which was a treatment identified by Carl Reichnbach in the 1850s. [17]
Mr. P. G Higgs traced the origin of the usage of paraffin wax to its discovery in 1830 in his paper "Utilization of Paraffin Wax and Petroleum Ceresin." Although its use was restricted for a long time, as time passed, its useful properties were universally acknowledged as of market value. Its combustibility, resistance to water, inertness, and good electrical properties allowed it to be used in variety of purposes. [18]
Video
Video of performing hand spa (paraffin wax treatment)
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 Paraffin wax(8002-74-2) Chemical Book. Web. accessed December 9, 2015.Unknown author
- ↑ Fisher Scientific UK Material Safety Data Sheet Paraffin wax Clayton State University. Web. Revised on March 16, 2007.
- ↑ WAXES: PARAFFIN CAMEO Chemicals. Web. accessed on December 14, 2015. Unknown author
- ↑ Alkane Types and Structurespetroleum.co.uk Web. accessed on January 13, 2016. Unknown author
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 WAX FACTSAmerican Fuel & Petrochemical Manufacturers. Web. accessed on December 15, 2015. Unknown author.
- ↑ 3.Chemical and Physical Properties Paraffin Deposition and Control. Web. accessed on December 15, 2015. Unknown author
- ↑ The Editors of Encyclopædia Britannica Paraffin wax Encyclopedia Britannica. Web. June 3, 2008
- ↑ Wax Refining The International Group, Inc.. Web. accessed on January 12, 2016. Unknown author.
- ↑ Chemical & Physical Properties Paraffin Project 409. Web. accessed on December 15, 2015. Unknown author.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Paraffin Wax for Arthritis WebMD. Web. accessed on December 15, 2015. Unknown author.
- ↑ Paraffin Waxcandlescience. Web. accessed on December 15, 2015. Unknown author
- ↑ Crayon How Products are Made. Web. accessed on December 15, 2015. Author unknown.
- ↑ The Story of Chewing Gum Ford Gum. Web. accessed on December 15, 2015. Author unknown.
- ↑ Rebecca Adams Petroleum Jelly May Not Be As Harmless As You Think Huffpost Style. Web. updated on October 23, 2013
- ↑ What is a paraffin pedicure wiseGEEK. Web. accessed on December 15, 2015. Unknown author.
- ↑ Paraffin Paula's Choice. Web. accessed on December 15, 2015. Unknown author
- ↑ Deborah Harding Facts on Paraffin Wax eHow. Web. accessed on January 13, 2016.
- ↑ History and Uses of Paraffin Wax nature. Web. published in January 19, 1935. Unknown author
| ||||||||||||||



