Hearing loss
Hearing loss refers to people who lose part or whole their ability of hearing due to the parts of their ears have been damaged or cannot function properly. Three types of hearing losses (conductive hearing loss, sensorineural hearing loss, and mixed hearing loss) that could exhibit different causes,symptoms and treatments, depending on the specific origin of the hearing loss. [1]
What is hearing loss?
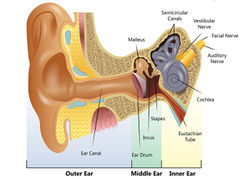
There are three types of hearing loss: (1) Conductive hearing loss; (2) Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL); (3) Mixed hearing loss.
(1) Conductive hearing loss: People who have conductive hearing loss because problems occur in the outer ear, the eardrum, or the ossicles. This loss influences the passage of the sound down to the ear drum to the inner ear. Additionally, conductive hearing loss may occur in company with the other two types of hearing loss.
(2) Sensorineural hearing loss: When the hair cells within the cochlea are damaged, or the vestibulocochlear is damaged, this type of hearing loss that may happen mainly refers to the deafness in the inner ear. The sensorineural is also called nerve-related hearing loss. [2]
(3) Mixed Hearing loss: This happens when the conductive and sensorineural hearing loss combine that may affect your outer, middle, and inner ears, even the auditory nerve. People who have mixed hearing loss could have a hard time recognizing and understanding the sound.[3]
Causes
Conductive hearing loss (problem conducting sound waves): Most common cause of this type of hearing loss is cerumen that builds up layers of wax in the outer ear blocks the passage for the sound, so the sound cannot reach the ear drum. When people get infected by bacteria or other diseases, the infection and inflammation in the outer ear could cause temporary hearing loss. Since the conductive hearing loss is due to problems in the middle ear or the inner ear, if the organs in these two parts of ears, such as ossicles, otosclerosis, otitis media, get inflammation or damaged by pressure or surgery, one’s ear could still lose their hearing ability. Specifically, when the fluid fills up the middle ear space and surrounds the ossicles, the ear drum cannot work properly to pass the sound to the inner ear. The uncommon and strange tumor in the ear can also cause conductive hearing loss.[4] The other situation where someone may have conductive hearing loss is due to their genetic inheritance. [5]
Sensorineural hearing loss: If one’s ear is exposed to extreme loud noise for such a long period, he may have the sensorineural hearing loss, which could be permanent or temporary depended on the sound level. People with a high fever, acoustic tumors, or stroke can all result in sensorineural hearing loss. Ear surgery rises a risk about losing hearing function that may apply to the other conductive hearing loss and mixed hearing loss as well.[4]The Meniere’s disease can also cause by accumulating fluid in the inner ear that builds up the pressure disabling the inner ear to balance other organs. People may feel tinnitus when that temporary hearing loss happened. Taking drugs which are ototoxic will damage the cochlea. Another factor that may contribute to this type of hearing loss is one’s age. According to an authoritative report, one of seven people who were more than sixty-five years old endures this annoying hearing loss.[2][3]
Mixed hearing loss: Just as its name implies, it is the mixed hearing loss that results from both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss; Therefore, it combines both causes within one. [3]
Signs and Symptoms
Some people who have hearing loss may not recognize they do. Therefore, be more careful if you have the following symptoms or signs because your body always warms you through various ways. Hearing loss could occur suddenly or developed gradually. If one has a tumor or becomes older, they need to more cautious and check with the doctor because their blood circulation will not go pretty well as normal, leading to a potential hearing loss. [1] Moreover, some more specific signs would be like listening and watching the television with a high volume. People may even find it difficult to talk to somebody else on their phone because they cannot hear them clearly. They try to avoid attending social events because it will be more challenging for them to listen in a noisy environment, and they have to ask others to repeat what they have said. In fact, people with the high-frequency hearing loss could miss a lot of different sounds, particularly young children or women’s voices. According to Brande’s research, he explains that “Certain consonant sounds like s, sh, f, v, th, f, p, making it difficult to understand some words” (“Hearing loss symptoms”). [6]
Treatment
Conductive Hearing Loss: Depended on the cause of the conductive hearing loss, treatment could be varied. The bone conduction hearing aid may help to make the correction of the congenital absence of ear canal and provide amplification by surgery. By implanting this help such as osseointegrated device into ears, people have chances to regain the ability to hear again. In addition, the severe infection such as chronic ear infections or chronic middle tumors needs to be taken away by surgeries. Doctors also utilize pressure equalizing tubes or antibiotics to treat infections. After the body of the patient who had a head trauma reaches the stabilization, doctors help them to gradually repair the broken structure of the middle ear and help it to function properly. Moreover, due to otosclerosis which commonly exists in early adulthood, the sound cannot reach the middle ear. Fortunately, in order to fix this damage, the patient just need to take a surgery to have a mobile stapes prosthesis rather than an immobile one. Since the measles virus is one cause of conductive hearing loss, measles vaccination can reduce the amounts of people who could have otosclerosis. [3]
Sensorineural Hearing Loss: For those who have acoustic trauma may lead to the sensorineural hearing loss. In order to eliminate the inflammation or intumescence of cochlear hair cell and heal the injured inner ear, people need to receive medical care related to corticosteroids. Besides, corticosteroids can also use to treat the sudden hearing loss generated from viral. Surgery can remove the toxins in the inner ear out if the inner ear fluid bursts suddenly and outpouring. Medical treatment such as long-term corticosteroids can be used to cure autoimmune inner ear disease which will take a few months to heal it finally. Food diet with less sodium and corticosteroids to medicate patients who have the family record of Meniere’s disease to eradicate vertigo. Doctors also use diuretics within this therapy. Plus, procedures can also cure vertigo. Removing benign tumors by surgeries via irradiation can help to improve the hearing loss. Patients may recover more than fifty percent of their hearing function after receiving the tumor removal in the premise the tumor is benign with a small size. Resulted from central nervous system, the sensorineural hearing loss can be treated by medical treatment regarding to the particular diseases. Cochlear implants or hearing aids can help people who have the irreversible sensorineural hearing loss. [3]
Treatments for Mixed Hearing Loss: Mixed hearing loss incorporates above-mentioned measures of treatment. In addition to those, receiving a treatment to the conductive component at the first place then working on curing sensorineural hearing loss after that will be a better order to treat mixed hearing loss. [3]
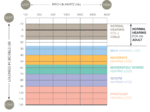
Degrees of hearing loss
- Mild hearing loss— 26 - 40 dB When a soft conversation or noisy background music is playing, people may have some difficulty to hear the sounds. They are able to hear sounds in a quite environment.
- Moderate hearing loss— 41 - 55 dB It’s harder for people who have the moderate hearing loss to understand conversations or speeches. If the patient listens to a woman or children who generally talk fast in a clamorous environment (restaurants or public places), he is hardly able to listen to their voices. When they listen to radio or watch the television, they need to turn it up in order to make the sound louder that could help them hear the sounds clearly. At this level, wearing the hearing aids could help people with the moderate hearing loss.
- Moderately-severe hearing loss— 56 - 70 dB Other people can recognize your hearing loss if you have the moderately-severe hearing loss. It will be hard for the patient to participate in group discussions and easily misunderstand words. For instance, the speaker could only catch one word, but the speaker says two or more words. The hearing aid is available to help people with this level of issue.
- Severe hearing loss— 71 - 90 dB At this level of hearing loss, people need to communicate with a loud and direct voice in order to allow the patient to understand what they speck. It will be not easy at all to have a conversation with one who has severe hearing loss. Sometimes people have to use their body language to convey the meaning. Severe hearing loss commonly accumulated from previous years of hearing loss and then the condition deteriorates. They have no choice but to wear the hearing aids if they still desire to hear sounds because normal or even louder voice sounds become inaudible.
- Profound Hearing loss— 91+ dB They cannot have any reaction to most of the sounds, including almost all daily sounds. The profound hearing loss influences the patient’s life a lot, resulting in struggling with the understanding of amplified speech, and all sounds will sound inaudible at this level. The patient needs to ask the doctors to seek help because the hearing aid is not enough to change this condition. [7] [8]
Degrees of hearing loss in children:
- Minimal hearing loss—16 - 25 dB Extremely soft conversation or speech may not be able to be detected by their ears. These kids have a little difficulty to hear softly sound from a long distance, but it will be an issue in their life that minimal hearing loss does not usually cause significant problems.
- Mild hearing loss—26 - 40 dB Comparing with the minimal hearing loss, the mild hearing loss is pretty much the same except these children cannot hear some sounds of certain words, particularly words or phrases ending with blurred sounds. Therefore, when children are in the noisy classroom or other places, it will be difficult for them to hear some words clearly. For this level of hearing loss in children, doctors usually recommend them to use hearing aids to help to improve the condition.
- Moderate hearing loss—41 - 55 dB As other people communicate with children who have moderate hearing loss, they may find that these kids miss over half of their conversation. In order to receive amplification, hearing aids are required to wear because the level of hearing loss will contribute to diminishing vocabulary and even unclear pronunciation of words. Without any help, the moderate hearing loss will limit children’s ability of communication and lack of monitoring their voices.
- Moderate to severe hearing loss—56 - 70 dB The majority of sounds become indiscernible to the children, so they cannot fully establish the ability of speech and language. In fact, the children need to seek help from speech and language therapists in order to develop these skills.
- Severe to profound hearing loss—71 dB and above Any effective interventions such as hearing aids can help with amplification of sounds because most sounds for children who have severe to profound hearing loss are inaudible. They may have to learn lip reading or sign language for the purpose of communication.
- High-frequency hearing loss—1,500 - 8,000 Hz It will be intensely difficult for children to receive sounds. They cannot recognize the low-frequency sounds from the background, and high frequency sounds from people’s speech or conversations. [9]
Video
This video exhibits the ongoing issue of hearing loss in the United States that The Hearing Loss Association of America estimated that by age 65, one out of three people in the U.S. has some degree of hearing loss. Besides, this video also reveals the main causes, symptoms of hearing loss, along with treatment and preventions.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Hearing Loss (cont.) ‘’eMedicineHealth. Web. last-accessed March 19, 2017
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 What is sensorineural loss? Hearing Link. Web. Mar 4, 2017.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Types, Causes and Treatment Hearing Loss Association of America. Web. Mar 3, 2017 at 12:37.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Hearing Loss Signs and Symptoms UCSF Medical Center. Web. Mar 5, 2017 at 17:20.
- ↑ What is conductive hearing loss? Hearing Link. Web. Mar. 2, 2017 at 17:35.
- ↑ Plotnick, Brande. Hearing loss symptoms Healthy Hearing. Web. September 22, 2016.
- ↑ Hearing Loss Carolina Hearing Doctors. Web. accessed-Mar. 17, 2017.
- ↑ Degrees of hearing loss Cochlea. Web. Last-accessed March 17, 2017.
- ↑ Degrees of Hearing Loss SIEMENS. Web. accessed-Mar. 17, 2017.
| ||||||||||||||||||||