Talk:Cesium
There is this picture of "solid and liquid caesium" on the article. The article states that caesium is a silvery-gold color. It is also an alkali metal, which is shiny like all metals. This description does not match with the appearance of the stone on the picture of "solid and liquid Caesium". That is why I had removed the picture. I strongly suspect that the stone is pollucite, the main ore of caesium. --Chemicalinterest (talk) 10:32, 5 December 2010 (PST)
- Yes - its certainly the mineral form. The source does not clarify. --Ashcraft - (talk) 12:51, 5 December 2010 (PST)
Parking original content for possible re-insertion... --Ashcraft - (reply) 13:17, 27 October 2017 (EDT)
| Cesium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Info | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic Symbol | Atomic symbol::Cs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic Number | Atomic number::55 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic Weight | Atomic weight::132.9054 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical series | alkali metals | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | silvery gold 
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group, Period, Block | 1, 6, s | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Xe] 6s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2,8,18,18,8,1 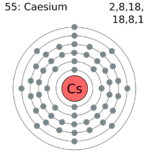
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS number | CAS number::7440-46-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density | Density::1.93 g/ml | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | Melting point::28.44 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | Boiling point::671 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of Cesium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All properties are for STP unless otherwise stated. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cesium (or caesium) is a chemical element of the alkali metal group with symbol Cs. German chemists Robert William Bunsen and Gustav Robert Kirchhoffin discovered Cesium 1860 in mineral water from Dürkheim, Germany. This metal looks like silvery gold and is both soft and ductile. It occurs in several minerals, but has a high cost per gram. Today, it is used in many different ways which are Atomic clocks, Vacuum tubes and so on. However, it contains risks because it can be easily explosive and if it put in water it will change to stronger base. [1]
Properties
Cesium is the chemical element in the periodic table with an atomic number of 55. Also known as Caesium, it has a chemical symbol of Cs. This metal looks like silvery gold and is both soft and ductile. It has a characteristic that compounds burn with blue color. When it reacts with water, it becomes explosive. Cesium is classified as a hazardous material because of high activity and is shipped in dry mineral oil or inert atmosphere, etc. [2]
Cesium is the most electropositive chemical element in the periodic table. Cesium’s melting point is 28.4°C. Caesium is instructed with 132.90 amu for atomic mass and it's hard to boiling because Caesium contain high boiling point which is 678.4°C. The crystal of structure is cubic with 1.873 g/cm3 density.[3]
Occurrences
An element of the alkali metal group, Cesium participates with Earth crust. It occurs in several minerals such as lepidolite, pollucite, amazonite, etc. One of the most important of these metals are located in Bernic Lake in Manitoba, Canada. In there, it is assumed to contain 350,000 metric tons of pollucite ore. [4] Among several minerals, Silicate mineral, and Lepidolite contain a lot of Cesium. It can be isolated by electrolysis in which pure and gas-free Caesium can be obtained. In 1970s, Cesium was very expensive, its price was almost $30 per gram.[5]
Uses
In the past, many people tried to find the important use of caesium in research and development, but they didn't find anything until 1920s. However, today Cesium is used in many different ways in the world. It associated with many sources such as Atomic clocks,removes air traces in vacuum tubes, ion propulsion systems, photoelectric cells, and so on. Atomic clock is known as nuclear clock, it uses measure for risk of catastrophic destruction. A form of electric propulsion, ion thruster, used the Coulomb force. Photoelectric cell(solar cell) makes energy from sunlight directly into electricity. [6]
Precautions
Caesium is one of the alkali metals. All alkali metals are risky because they are one of the most reactive and explosive. When it comes into contact with water, the risk is increased. Caesium is very strong base, easily corrodes and it is sometimes get fired in air without catalyst. The hydrogen gas also reacts violent explosion by contact with water like other alkali metals. However, caesium is more powerful by cold water or ice. Caesium also is most explosive metal, so it requires special care in its storage and transport.[7]
References
- The Element Cesium C.R. Hammond, unknown publisher.
- Caesium Wikipedia.org, Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.
- The Element Cesium Unknown author.
- Cesium Periodic Table v2.5 since 1/2/99.
- Caesium - Occurrence Encyclopedia Wikimedia Foundation, Inc.

