
No higher resolution available.

|
This image was uploaded to the shared "Image Pool" and is usable on any CreationWiki site.
Please go to the Pool to edit its description.
|
Summary
Glacial Lake Missoula was formed when a finger of the Cordilleran ice sheet crept southward into the Idaho panhandle, forming a large ice dam that blocked the mouth of the Clark Fork River, creating a massive lake 2,000 feet deep and containing more than 500 cubic miles of water. Glacial Lake Missoula stretched eastward for some 200 miles and contained more water than Lake Erie and Lake Ontario combined. When the highest of these ice dams failed, lake water burst through, shooting out at a rate 10 times the combined flow of all the rivers of the world. This towering mass of water and ice literally shook the ground as it thundered toward the Pacific Ocean, stripping away hundreds of feet of soil and cutting deep canyons -- "coulees" -- into the underlying bedrock. With flood speeds approaching 65 miles per hour, the lake would have drained in as little as 48 hours.
Copyright status:
This image is public domain because it was first published by the U.S. Geological Survey.
Source:
http://vulcan.wr.usgs.gov/LivingWith/Historical/LewisClark/Maps/map_missoula_floods.html
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment |
|---|
| current | 00:38, 2 April 2009 | 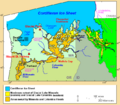 | 666 × 580 (26 KB) | Ashcraft | Glacial Lake Missoula was formed when a finger of the Cordilleran ice sheet crept southward into the Idaho panhandle, forming a large ice dam that blocked the mouth of the Clark Fork River, creating a massive lake 2,000 feet deep and containing more than |
File usage
The following page uses this file:

